Processing Request...
Processing Request...


Art directors are responsible for the visual style and images in magazines, newspapers, product packaging, and movie and television productions. They create the overall design of a project and direct others who develop artwork and layouts.
Learn More

Broadcast and sound engineering technicians set up, operate, and maintain the electrical equipment for radio and television broadcasts, concerts, sound recordings, movies and in office and school buildings.
Learn More
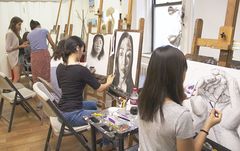
Craft and fine artists use a variety of materials and techniques to create art for sale and exhibition. Craft artists create handmade objects, such as pottery, glassware, textiles or other objects that are designed to be functional. Fine artists, including painters, sculptors, and illustrators, create original works of art for their aesthetic value, rather than for a functional one.
Learn More

Dancers and choreographers express ideas and stories, using dance. There are many types of dance such as ballet, tango, modern dance, tap, and jazz.
Learn More

Fashion designers create original clothing, accessories, and footwear. They sketch designs, select fabrics and patterns, and give instructions on how to make the products they designed.
Learn More

Film and video editors and camera operators record images that entertain or inform an audience. Camera operators capture a wide range of material for TV shows, motion pictures, music videos, documentaries, or news and sporting events. Editors construct the final productions from the many different images camera operators capture. They collaborate with producers and directors to create the final production.
Learn More
.jpg)
Game designers design graphics for game art and maps includes animating the characters and designing any virtual reality environments used, while game developers work on teams to plan, design, and produce video games for computers, mobile devices, or game consoles.
Learn More

Graphic designers create visual concepts, by hand or using computer software, to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, or captivate consumers. They develop the overall layout and production design for advertisements, brochures, magazines, and corporate reports.
Learn More

Multimedia artists and animators create animation and visual effects for television, movies, video games, and other forms of media.
Learn More

Music directors (also called conductors) lead orchestras and other musical groups during performances and recording sessions. Composers write and arrange original music in a variety of musical styles.
Learn More

Photographers use their technical expertise, creativity, and composition skills to produce and preserve images that visually tell a story or record an event.
Learn More

Producers and directors create motion pictures, television shows, live theater, and other performing arts productions. They interpret a writer’s script to entertain or inform an audience.
Learn More

Take our free psychometry test to discover your passion and potential!
Try It Now!

Book a campus tour through us!
Book Now!

Submit your result to Edumetry, and a list of scholarship that is eligible for your result will be filtered out for you!
Match Now!